OPERATING SYSTEM – OVERVIEW:
An Operating
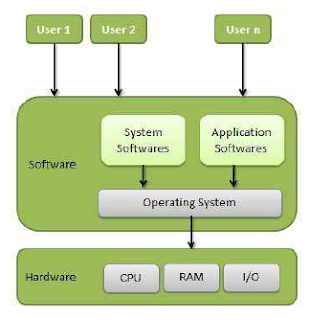
System (OS) is an interface between a computer user and computer hardware. An operating system is a software which performs all the basic tasks like file management,
memory management, process management, handling input and output, and controlling
peripheral devices such as disk drives and printers. Some popular
Operating Systems include Linux Operating System, Windows Operating System, VMS, OS/400, AIX, z/OS, etc.
DEFINITION
An operating
system is a program that acts as an interface between the user and the computer hardware and controls the
execution of all kinds of programs.
Following are
some of important functions of an operating System.
1.
Memory Management
2.
Processor
Management
3.
Device
Management
4.
File Management
5.
Security
6.
Control over
system performance
7.
Job accounting
8.
Error detecting
aids
9.
Coordination
between other software and users
Memory
Management
Memory
management refers to management of Primary Memory or Main Memory. Main memory is a
large array of words or bytes where each word or byte has its own address. Main memory
provides a fast storage that can be accessed directly by the CPU. For a program to be
executed, it must in the main memory. An Operating System does the following
activities for memory management:
1.
Keeps tracks of
primary memory, i.e., what part of it are in use by whom, what part are not in
use.
2.
In
multiprogramming, the OS decides which process will get memory when and how
much.
3.
Allocates the
memory when a process requests it to do so.
4.
De-allocates
the memory when a process no longer needs it or has been terminated.
Processor
Management
In
multiprogramming environment, the OS decides which process gets the processor
when and for how
much time. This function is called process scheduling. An Operating
System does the
following activities for processor management:
1.
Keeps tracks of
processor and status of process. The program responsible for this task is known
as traffic controller.
2.
Allocates the
processor (CPU) to a process.
3.
De-allocates
processor when a process is no longer required.
Device
Management
An Operating
System manages device communication via their respective drivers. It does the following
activities for device management:
1.
Keeps tracks of
all devices. The program responsible for this task is known as the I/O
controller.
2.
Decides which
process gets the device when and for how much time.
3.
Allocates the
device in the most efficient way.
4.
De-allocates
devices.
File
Management
A file system
is normally organized into directories for easy navigation and usage. These directories may contain files and
other directions.
An Operating
System does the following activities for file management:
1.
Keeps track of
information, location, uses, status etc. The collective facilities are often
known as file system.
2.
Decides who
gets the resources.
3.
Allocates the
resources.
4.
De-allocates
the resources.
Other
Important Activities
Following are
some of the important activities that an Operating System performs:
1.
Security --
By means of password and similar other techniques, it prevents unauthorized
access to programs and data.
2.
Control over
system performance -- Recording delays between request for a service and response from
the system.
3.
Job accounting --
Keeping track of time and resources used by various jobs and users.
4.
Error detecting
aids -- Production of dumps, traces, error messages, and other debugging
and error detecting aids.
5.
Coordination
between other software and users -- Coordination and assignment of
compilers, interpreters, assemblers and other software to the various users of
the computer systems.






0 comments :
Post a Comment