Operating System ─ Linux:
Linux is one of
popular version of UNIX operating System. It is open source as its source code
is freely available. It is free to use. Linux was designed considering UNIX compatibility.
Its functionality list is quite similar to that of UNIX.
Components
of Linux System
Linux Operating
System has primarily three components
1.
Kernel -
Kernel is the core part of Linux. It is responsible for all major activities of
this operating system. It consists of various modules and it interacts directly
with the underlying hardware. Kernel provides the required abstraction to hide
low level hardware details to system or application programs.
2.
System Library -
System libraries are special functions or programs using which application
programs or system utilities accesses Kernel's features. These libraries implement
most of the functionalities of the operating system and do not requires kernel
module's code access rights.
3.
System Utility -
System Utility programs are responsible to do specialized, individual level tasks.
Kernel
Mode vs. User Mode
Kernel
component code executes in a special privileged mode called kernel mode with
full access to all resources of the computer. This code represents a single
process, executes in single address space and do not require any context switch
and hence is very efficient and fast. Kernel runs each processes and provides
system services to processes, provides protected access to hardware to
processes. Support code which is not required to run in kernel mode is in
System Library. User programs and other system programs works in User Mode which
has no access to system hardware and kernel code. User programs/ utilities use
System libraries to access Kernel functions to get system's low level tasks.
Basic
Features
Following are
some of the important features of Linux Operating System.
1.
Portable -
Portability means software can work on different types of hardware in same way.
Linux kernel and application programs supports their installation on any kind
of hardware platform.
2.
Open Source -
Linux source code is freely available and it is community based development
project. Multiple teams work in collaboration to enhance the capability of
Linux operating system and it is continuously evolving.
3.
Multi-User -
Linux is a multiuser system means multiple users can access system resources like
memory/ ram/ application programs at same time.
4.
Multiprogramming
- Linux is a multiprogramming system means multiple applications
can run at same time.
5.
Hierarchical
File System - Linux provides a standard file structure in which system files/
user files are arranged.
6.
Shell -
Linux provides a special interpreter program which can be used to execute commands
of the operating system. It can be used to do various types of operations, call
application programs. etc.
7.
Security -
Linux provides user security using authentication features like password protection/
controlled access to specific files/ encryption of data.
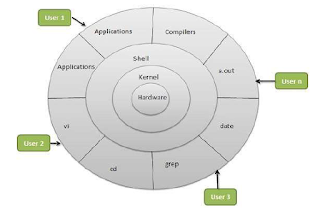
Architecture
The following illustration shows the
architecture of a Linux system:
The
architecture of a Linux System consists of the following layers:
- Hardware layer - Hardware consists of all peripheral devices (RAM/ HDD/ CPU etc.).
- Kernel – It is the core component of Operating System, interacts directly with hardware, provides low level services to upper layer components
- Shell - An interface to kernel, hiding complexity of kernel's functions from users. The shell takes commands from the user and executes kernel's functions.
- Utilities - Utility programs that provide the user most of the functionalities of an operating systems.






0 comments :
Post a Comment